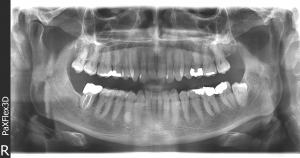
Periodontal (gum) diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis.
These are serious infections that, left untreated, can lead to tooth loss. The word periodontal means “around the tooth.” Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the gums and bone supporting the teeth. Periodontal disease can affect one tooth or many teeth. It begins when the bacteria in plaque (the sticky, colourless film that constantly forms on your teeth) causes the gums to become inflamed.
Causes of Periodontal Disease:
1. bacterial Plaque
2. Genetics
3. Smoking
4. Puberty, Pregnancy, Menopause
5. Stress
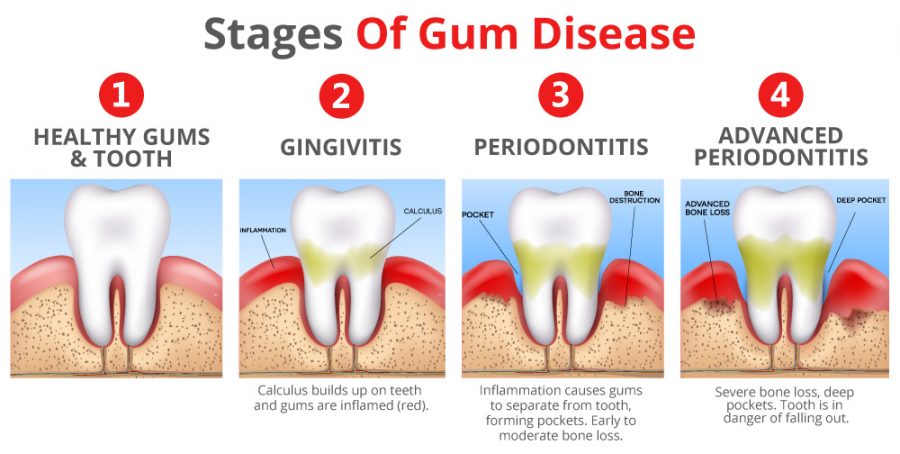
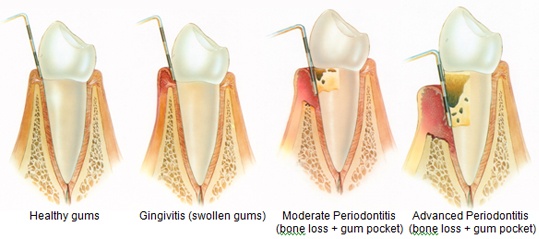
Gingivitis is the mildest form of periodontal disease. It causes the gums to become red, swollen, and bleed easily.
There is usually little or no discomfort at this stage. Gingivitis is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care. We recommend a 6 monthly Interval for Hygienist Treatments.
Aggressive periodontitis occurs in patients who are otherwise clinically healthy. Common features include rapid attachment loss and bone destruction and familial aggregation.
Chronic periodontitis results in inflammation within the supporting tissues of the teeth, progressive attachment and bone loss. This is the most frequently occurring form of periodontitis and is characterized by pocket formation and/or recession of the gingiva. It is prevalent in adults but can occur at any age. Progression of attachment loss usually occurs slowly, but periods of rapid progression can occur.
Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic diseases often begins at a young age. Systemic conditions such as heart disease, respiratory disease, and diabetes are associated with this form of periodontitis.
Necrotizing periodontal disease is an infection characterized by necrosis of gingival tissues, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. These lesions are most commonly observed in individuals with systemic conditions such as HIV infection, malnutrition and immunosuppression.
Deep Scaling and Soft tissue Laser Treatment
We are treating Periodontal Disease using conventional deep scaling and root planning and use a soft tissue laser to initiate the formation of a new connection (epithelium) of the gum to the teeth.
Clear stabilization splints and Chlorhexidine gel trays are also used to achieve outstanding results.
Gum Disease Treatment at Atlantic Dental
If you want to know more, please call 01637852888 or contact us ONLINE.
How is Gum Disease treated?
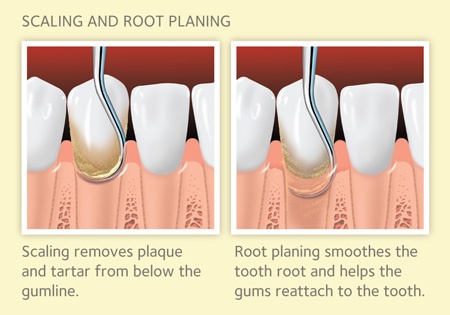
Deep Scaling and Root Planing will be carried out under local anaesthesia and is usually painless. The aim is to remove or disrupt the “Biofilm” (layer of bacteria covering the affected teeth. Once the biofilm is removed the root surfaces are smoothed and the gum can heal.
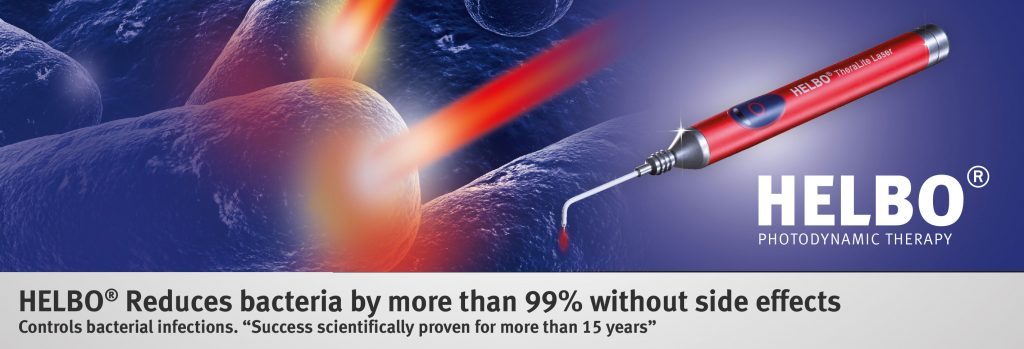
Antibiotics and Laser
In combination with mechanical removal of the bacterial layer (biofilm), Antibiotic Therapy might be indicated. An alternative treatment is the use of a Laser (Photodynamic Therapy) to eliminate pathogenic bacteria. At Atlantic Dental we are using the HELBO system from Bredent (see picture below).